If you have recently installed arch linux on your computer and have no idea about what to do next? This article is going to help with the post-installation setup where I will show you the top 10 things you must do after installing arch linux. I will guide you through the crucial steps needed to optimize the arch linux system in 2023. Lets get started.
Update the System
The first thing to do after installing arch linux is to update the system by running a command in the terminal, which fetches the latest package information and upgrades all packages.
sudo pacman -SyuNext, it is recommended to install core package tools like nano, git, and other necessary packages for a smooth experience.
sudo pacman -S nano git vim neofetchConfigure PacMan and mirrors
It’s time to configure your pacman and mirror list to enhance the package installation experience. First, you need to modify your Pacman configuration file by uncommenting some lines and adding “ILoveCandy” to make the progress bar look like Pacman eating the dots.
sudo nano /etc/pacman.conf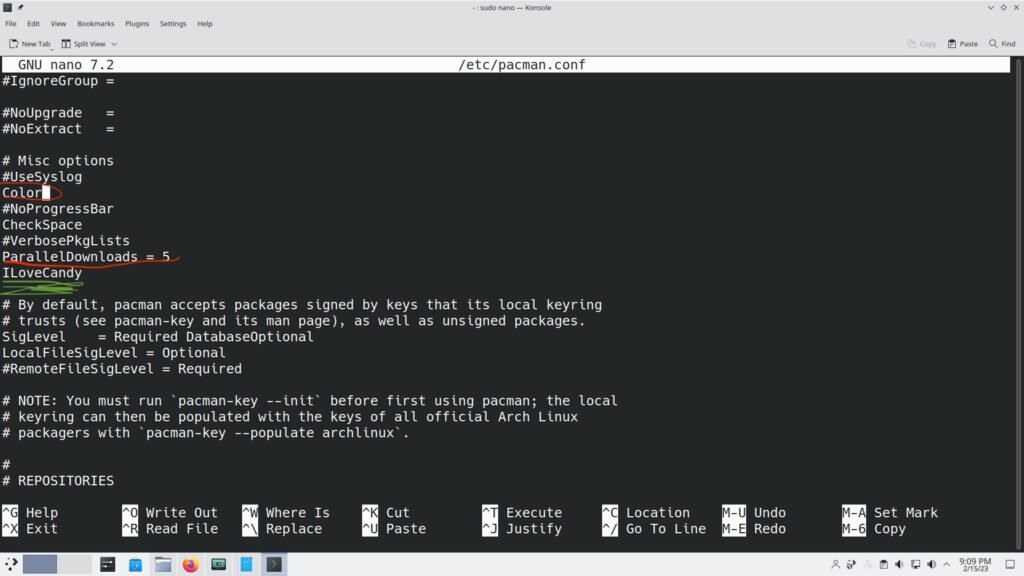
After saving the changes, update the Pacman by running this command.
sudo pacman -SyYou will now see colored text and a Pacman progress bar while installing any package.
If you face slow download speeds, you can update the mirror list with the fastest servers available. Install Reflector by running a command.
sudo pacman -S reflectorThen, create a backup file of the default mirror list.
sudo cp /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist.bakThen run the below command to fetch the top 10 fastest servers, which will add them to the mirror list.
sudo reflector --verbose --latest 10 --protocol https --sort rate --save /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlistThen update the pacman by running this command.
sudo pacman -SyAfter running any command to install a package via pacman, you should experience improved download speeds while installing packages.
Note: You can also use reflector to retrieve a fastest mirrors from a specific country.
sudo reflector --verbose --country 'India' -l 5 --sort rate --save /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlistThe above command sets the mirror preferred location and retrieves the top 5 mirrors of India and sorts them by download rate. Check countries list:
reflector --list-countriesSetup GUI Desktop
Setting up a desktop environment in Arch Linux can seem like a daunting task, but it is quite simple if you follow a few steps. Arch Linux provides several desktop environments, such as GNOME, KDE, XFCE, and more, so you can choose the one that suits your preferences.
Set Up Display server:
sudo pacman -S xorgSet Up Gnome Desktop Environment
sudo pacman -S gnome gnome-extra gnome-tweaks gdm sudo systemctl enable gdm.servicesudo systemctl start gdm.serviceSetup Plasma Desktop Environment
sudo pacman -S plasma plasma-wayland-session kde-applications sddmsudo systemctl enable sddm.servicesudo systemctl start sddm.serviceSetup XFCE Desktop Environment
sudo pacman -S xfce4 xfce4-goodies sddmsudo systemctl enable sddm.servicesudo systemctl start sddm.serviceInstall Important Tools
Installing essential packages can greatly improve your experience with Arch Linux, and there are a few commands you can run to add Bluetooth support and install some useful tools. By running these commands one by one, you can easily add Bluetooth support to your Arch Linux system.
sudo pacman -S bluez blueman bluez-utilssudo modprobe btusbsudo systemctl enable bluetooth && sudo systemctl start bluetoothOnce you’ve added Bluetooth support, you can then run a command to install some useful packages that can make your life easier. These packages can include various utilities, tools, and software that can help streamline your workflow and make it easier to perform various tasks.
sudo pacman -S p7zip unrar tar rsync git neofetch htop exfat-utils fuse-exfat ntfs-3g flac jasper aria2 In addition to installing these useful packages, it is also recommended that you set up a Java environment on your Arch Linux system.
sudo pacman -S jdk-openjdkAll users with an AMD or Intel CPU should install the microcode updates to ensure system stability.
Intel
sudo pacman -S intel-ucodeAMD
sudo pacman -S amd-ucodeThen update grub ;
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfgInstall Aur Helper & Flatpak
While using Pacman in Arch Linux, you may find that there are limitations on which GUI applications you can install. For example, popular programs like Google Chrome, VSCode, and Timeshift cannot be installed through Pacman. Instead, you will need to rely on the Arch User Repository (AUR) or Flatpak to install additional software.
Yay is a popular aur helper, which simplifies the process of installing and managing packages from AUR.
To install Yay, run this command to install some dependencies.
sudo pacman -S --needed base-devel gitThen clone the GitHub repository by typing this command.
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/yay.gitThen navigate to the Yay directory
cd yayRun this command to install yay:
makepkg -siOnce Yay is installed, you can start installing GUI applications. For example, you can search for VSCode & install it by running the below commands
yay -Ss vscodeyay -S visual-studio-code-bin It’s also recommended to set up Flatpak in Arch Linux, which you can do by running this command.
sudo pacman -S flatpakMust Install GUI apps
It’s time to install some useful applications that will enhance your basic workflow on Arch Linux. You can go ahead and install applications like Firefox, LibreOffice, VLC, GIMP, and Thunderbird.
sudo pacman -S firefox libreoffice-fresh vlc gimp thunderbird kdenlive krita Get additional kernels
In Arch Linux, it’s a good idea to have multiple kernels installed as a safety precaution. If one kernel fails to boot, you can use another one to start the operating system. For instance, I suggest installing the LTS kernel by running a command, as it’s generally considered to be more stable than the latest kernels. Additionally, you can explore other kernels like Zen and Hardened.
sudo pacman -S linux-lts linux-lts-headerssudo pacman -S linux-hardened linux-hardened-headerssudo pacman -S linux-zen linux-zen-headersUse Timeshift
TimeShift is a backup tool for Arch Linux that can save you from losing important data in case of system failure. It’s very similar to Windows system restore and macOS time machine. TimeShift allows you to take a snapshot of your current system and restore it in case of issues. You can install time shift by running this command:
yay -Sy timeshiftSetup firewall
An uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is a security tool that can help protect your computer from network traffic and block malicious software from accessing your network via the internet. To set up a firewall:
sudo pacman -S ufwsudo systemctl enable ufwsudo systemctl start ufwUFW allows you to have full control over enabling and disabling ports. For example, if you’re running an SSH server on port 22, you can disable this port to prevent connections from remote computers.
sudo ufw deny 22/tcpSpeedUp App Launch With PreLoad
Preload is a daemon service that runs in the background. It Analyzes the user behavior and tracks what applications are frequently running by the user.
Based on these analyses, it predicts what applications the user might run next and fetches those binaries and their dependencies into memory and hence increasing the start-up time of the applications.
You Can install the preload by running the below commands.
yay -S preloadsudo systemctl enable preload && sudo systemctl start preloadBonus: Use AutoCpu Freq
Some users on some specific hardware may notice a higher battery consumption rate on Arch Linux than on Windows. This could be noticeable on the laptops. The easiest thing you can solve this problem on arch linux is simply installing auto-cpufreq. This is a very useful tool that actively monitors the battery state, CPU usage, and temperatures, ultimately allowing you to improve battery life without making any compromises.
Conclusion
That’s pretty much it, these are the top 10 things you must do after installing arch linux. If you have any suggestions or queries do let me know in the comments section below.