If you have just installed Fedora on your computer and aren’t unsure what to do next? This video will help you with post-installation setup. I will show you the top 10 essential things you must do after installing the Fedora workstation in 2024. I will guide you through the crucial steps to optimize the fedora workstation setup. So, without a further do let’s get started.
Configure DNF
The first thing you should do after installing the Fedora workstation is to configure the DNF package manager.
You can modify the DNF Config file to speed up package downloads.
sudo nano /etc/dnf/dnf.conf
Add the below lines at the end of the file:
max_parallel_downloads=10
fastestmirror=1Once done press ctrl + x, then Y, and press enter to save the changes.
Install Software / Firmware Updates
After configuring DNF, update your system by running this command.
sudo dnf updateIf In case your hardware manufacturer supports special firmware updates for linux, run these commands one by one:
sudo fwupdmgr refresh --forcesudo fwupdmgr get-updatessudo fwupmgr updateOnce everything is updated, reboot your system by running this command.
Use DNF5
DNF 5 is an advanced version of the DNF package manager and has been included in recent Fedora releases in the repository. It will be the default in future versions of Fedora, but you can start using it now in Fedora 40 to take advantage of its faster performance.
Simply run the below command to set up DNF5.
sudo dnf install dnf5 dnf5-pluginsAdding RPM Repositories
It’s always recommended to enable third–party repositories. Open the Software Center and If you see a pop-up asking to add third-party repositories, choose to enable them.
If not, click the hamburger icon, go to software repositories, and enable Fedora’s third–party repositories.
Additionally, you should enable RPMFusion repositories for Fedora via the command line. Run these commands one by one.
sudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpmsudo dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpmsudo dnf upgrade --refreshThese repositories provide stable and tested packages for Fedora, so it is highly recommended to enable them.
Switch Between Wayland Or XORG
By default, Fedora With Gnome Desktop uses the Wayland display server. If your PC or laptop has a Discrete Graphic card that struggles with WAYLAND protocol, you can switch to the legacy X11 protocol. To do so, log in, click on your username, then click the settings gear icon in the bottom right corner and choose GNOME XORG.
Using this setting, you can switch between XORG or Wayland seamlessly. Once selected, log back in.
Customize With GNOME Tweaks And Extensions Manager
Gnome-Tweaks & the extension manager allow you to customize and control the gnome desktop environment. Install gnome-tweaks & extension manager by running this command.
sudo dnf5 install gnome-tweaksflatpak install flathub com.mattjakeman.ExtensionManagerThen, open the tweaks application to customize the user interface. For example, Select Windows from the sidebar then you can enable or disable the maximize & minimize window buttons.
Additionally, You can also use the Windows section & enable Center new Windows, to have applications open in the center of the screen.
You can also use the extensions manager to install GNOME Extensions that enhance your desktop experience. I recommend installing these extensions to create a more futuristic gnome experience.
Blur My Shell / Burn My Windows / Astra Monitor / Caffeine / User ThemesMust Install Apps / Packages / Fonts
Installing essential packages, apps, and fonts can improve your fedora experience. Run the following command to install some recommended packages.
sudo dnf5 install fastfetch mpv wget git gcc make python3 python3-pip unrar unzip cargo p7zip p7zip-plugins ntfs-3g htop java-17-openjdk android-tools vlcIt’s time to install some useful GUI applications that will enhance your basic workflow on Fedora. You can go ahead and install applications like obs, transmission, mission center, spotify & more.
flatpak install flathub com.obsproject.Studioflatpak install flathub io.missioncenter.MissionCenterflatpak install flathub com.transmissionbt.Transmissionflatpak install flathub com.spotify.ClientTimeShift
Additionally, it’s highly recommended to install Timeshift for backups. You can install Time shift by running this command.
sudo dnf5 install timeshiftIt’s highly recommended to take a snapshot or backup of your system’s current state. This can help you restore your system to a previous state if something goes wrong, saving you from having to reinstall the operating system.
And lastly, run this command to install the most essential fonts.
sudo dnf install dejavu-sans-fonts dejavu-serif-fonts dejavu-sans-mono-fonts liberation-sans-fonts liberation-serif-fonts liberation-mono-fonts google-noto-sans-fonts google-noto-serif-fonts google-noto-mono-fontsInstall NVIDIA Drivers (Optional)
If your computer has an NVIDIA graphics card, it’s recommended to install the proprietary drivers instead of the default open-source Nouveau drivers, which don’t fully utilize your GPU. To check if your GPU is detected, run:
lspci | grep VGAAs you can see, it has detected my graphic card. I am gonna run this command to install default NVIDIA proprietary drivers.

sudo dnf install akmod-nvidia Once it’s done reboot your computer.
Run Local LLMS Like ChatGPT
In the world of generative AI tools, you can install and run chat GPT like LLMS offline on fedora using Ollama. It is a free and open-source tool that helps run large language models locally. You can Run LLAMA3, Mistral, Tiny LLaMA, and other models.
Simply head over to this link, copy this code paste it inside the terminal, and run the script. This will set up OLLAMA in a few minutes.
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh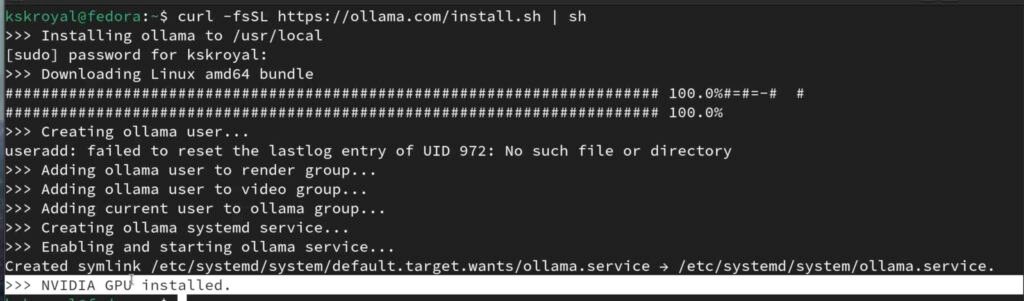
Notice that it has detected NVIDIA GPU on my computer and uses it to generate faster output. Now, let’s try installing LLAMA3 by running this command.
ollama run llama3.1Congratulations, now you can ask anything to the model like ChatGPT to find the answers, and works without the internet.
Improve battery life
Fedora is optimized more for desktops than laptops, so it might not offer the best battery life by default.
So it’s recommended to adjust the power setting to optimize the battery life on laptops by installing the advanced power management tool TLP. Run the below commands to setup TLP:
sudo dnf5 install tlpsudo systemctl enable tlpsudo systemctl start tlpWhile TLP can extend battery life, it may also disable certain features like turbo boost. AutoCPUfreq is a tool designed to replace TLP for improved battery life and performance.
It actively monitors battery state, CPU usage, and temperatures to optimize battery life without compromising performance. If TLP isn’t working for you, uninstall it with this command.
sudo dnf5 remove tlpThen copy the below code and paste it inside the terminal.
git clone https://github.com/AdnanHodzic/auto-cpufreq.git
cd auto-cpufreq && sudo ./auto-cpufreq-installerAfter installation, open the GUI tool from the app drawer and activate it to run as a daemon service. It uses a default profile to balance performance and battery life.
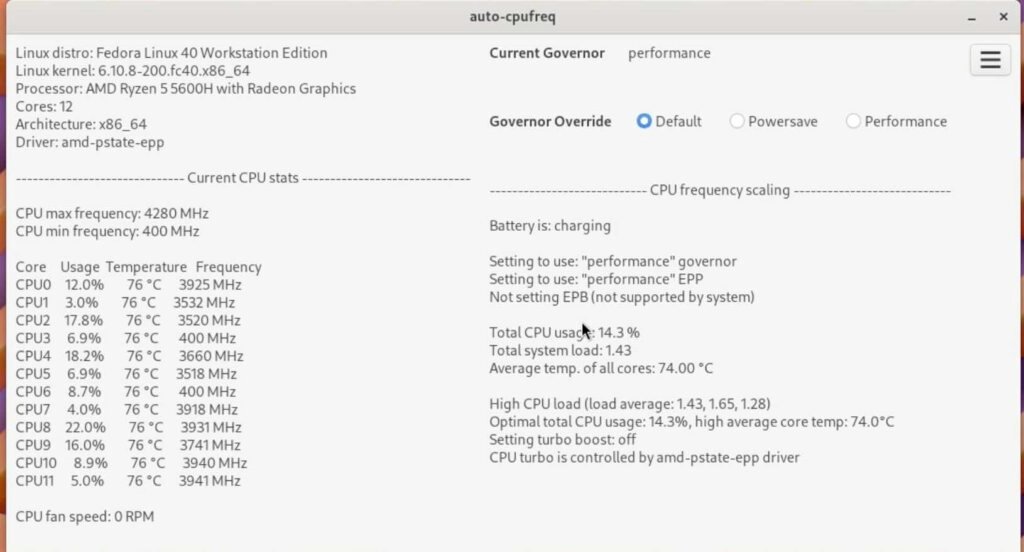
For peak performance, enable Performance mode, and for longer battery life, enable Power Save mode.